What Are All The Animals Who Can Get Blackleg


Cabbages tin autumn victim to an array of diseases from all of the major classes of pathogens – fungi, h2o molds, bacteria, and viruses.
The infections can range in severity from the unsightly just not usually fatal, such every bit powdery mildew, to the almost uniformly fatal bacterial soft rot.
Some of these pathogens live in the soil where they can readily attack the roots of your crop, and many others lurk in the cruciferous weeds growing nearby.

Nosotros link to vendors to assist you find relevant products. If yous buy from one of our links, nosotros may earn a committee .
Read on to learn about the many diseases that tin impact your cabbage ingather, and steps you tin can accept to foreclose or command them.
Common Cabbage Diseases
- Alternaria Foliage Spot
- Bacterial Leaf Spot
- Bacterial Soft Rot
- Blackleg
- Black Rot
- Bottom Rot
- Clubroot
- Downy Mildew
- Mosaic Virus
- Phytophthora Root Rot
- Powdery Mildew
- Band Spot
- White Mold
- Yellows
one. Alternaria Leaf Spot
Alternaria leaf spot is caused by 2 species of fungi, Alternaria brassicicola and A. brassicae.
Both species are well known for causing foliage spots to develop on older tissue, but these fungi tin can too infect the base of the developing heads.
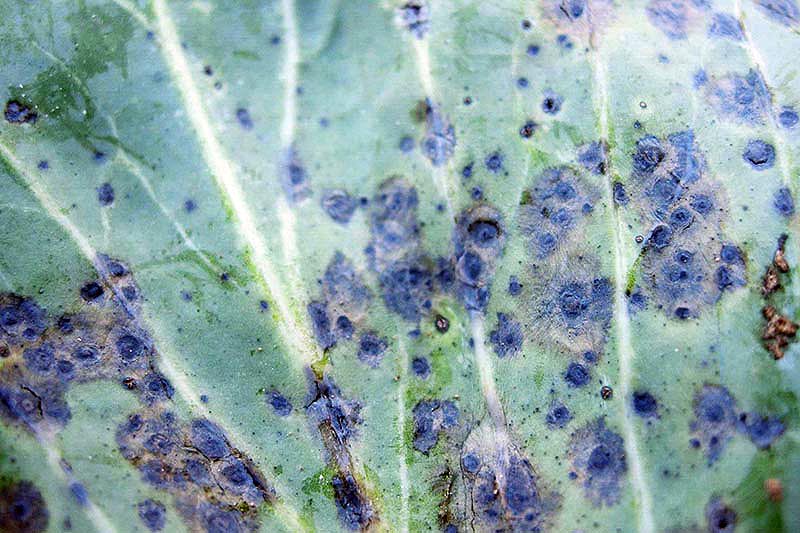

Alternaria is more than likely to cause affliction when moisture is present on the cabbage, and temperatures range from 68 to 81°F.
Symptoms include yellow spots that grow larger and develop rings around them similar a target or bull's-eye. As the tissue dies, the centers may autumn out, resulting in holes in the foliage. Equally the disease develops, the spots bring together together to form large areas of dead tissue.
Controls for Alternaria leaf spot outset with skillful cultural practices. These include the utilise of drip irrigation, sanitizing your gardening tools, rotating your crops, and removing all dead plant cloth at the stop of the growing season.
Biopesticides that may testify effective in the case of an outbreak include Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis .
2. Bacterial Leaf Spot
There are two dissimilar species of leaner that can cause bacterial foliage spot in cabbage, Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola and Xanthomonas campestris pv. armoraciae.
P. syringae pv. maculicola tin infect all types of cole crops. It causes spots to form on the leaves that start out small, becoming dark brown or purple as they increase in size.
These spots can join together to form angular lesions, which make the leaves expect ragged. In the instance of a severe infection, the foliage tin can die.
Unfortunately, this grade of bacterial leaf spot is readily spread past splashing water, including irrigation water, and by insects. This disease is almost prevalent during periods of absurd, wet weather.
In dissimilarity, X. campestris pv. armoraciae is more than probable to cause infections in warmer temperatures.
Initial symptoms include nighttime flecks on the leaves that spread into lesions. The centers often dethrone with time, resulting in round holes in the leafage.
Prevention and command efforts range from planting heat-treated seed to irrigation practices that minimize the corporeality of moisture that comes in contact with the leafage. Crop rotation is also critical in subsequent seasons, as the leaner can overwinter in the soil.
3. Bacterial Soft Rot
Bacterial soft rot is acquired by the the leaner Pectobacterium spp. (formerly Erwinia) and tin event in losses in a tremendous number of crops, including cabbage.
In fact, it is one of the most dissentious plant diseases known throughout the world.
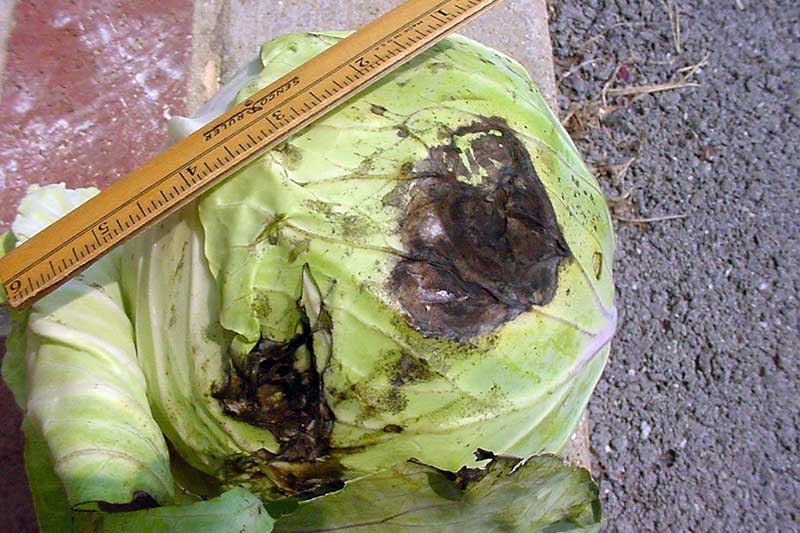

Cabbages tin bear witness symptoms in the field, but the majority of infections occur during storage.
The get-go signs of infection are pocket-size lesions that appear water soaked. They chop-chop overstate, and infected constitute tissue turns brown and mushy.
Ofttimes, the whole plant may decay.
The leaner that cause soft rot infect plants near readily in warm, humid conditions. Plants are easily infected, considering the bacteria live in the soil.
Even if temperatures are cool and less conducive to infection, the bacteria can nevertheless infect through wounds in constitute tissue, including those caused past insect damage.
The bacteria is spread by splashing water, gardening tools, and insects like cabbage maggots. In addition, plants that are already diseased with blackleg or blackness rot tin contract soft rot as a secondary infection.
There are a number of steps you tin take to minimize the chances of your cabbages being infected, ranging from avoiding harvesting crops in wet conditions to removing whatsoever soil with a dry out cloth before you store the heads.
Read more most bacterial soft rot here.
four. Blackleg
Blackleg is caused by a fungus, Phoma lingam, and it destroys the roots of many types of crops.
Young seedlings may develop pale, irregular spots on their leaves or stems, which can become round or oval with gray centers. As the symptoms spread, spots can develop on the underside of the leaves.
In the instance of a severe infection, the young cabbages will exist stunted and plants will often wilt, although the leaves remain fastened.
Initial symptoms of blackleg – such as light dark-brown, sunken cankers – can be seen at the base of the stems.
If infected cabbages are harvested and put in storage, dark brown or black spots tin develop on the leaves.
Infected seeds can be a source of this fungus, and it tin can survive in crop droppings. Cruciferous weeds can also serve as hosts. If the levels of seed infection are low merely the weather is favorable for disease, astringent losses can still occur.
The pathogen can spread by splashing water from rain or irrigation, and information technology can also be transmitted on gardening tools. In addition, spores on infected plants can be blown for miles in the air current.
And to brand things worse, secondary infections frequently follow cases of blackleg. These can include white mold and bacterial soft rot.
There isn't much y'all can exercise if your ingather is infected, so taking steps to prevent information technology is crucial.
Remove any cruciferous weeds, like wild radish, yellow cress, or wild mustard. Kickoff with seed from a reputable source that has been shown to be costless of the pathogen.
Space plants widely in the garden, so adequate airflow is readily available, and they will quickly dry later rain or dew.
Remove infected ingather debris from the garden as soon every bit possible. Dispose of it in the garbage, rather than on your compost pile.
Rotate crops for three to four years, and avoid planting other brassicas nigh where you plan to grow your cabbage.
5. Black Rot
Black rot, acquired past the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, affects a range of cole crops, and it can really practise a number on cabbage.
Severely infected plants volition accept smaller heads, and their outer leaves may die dorsum.
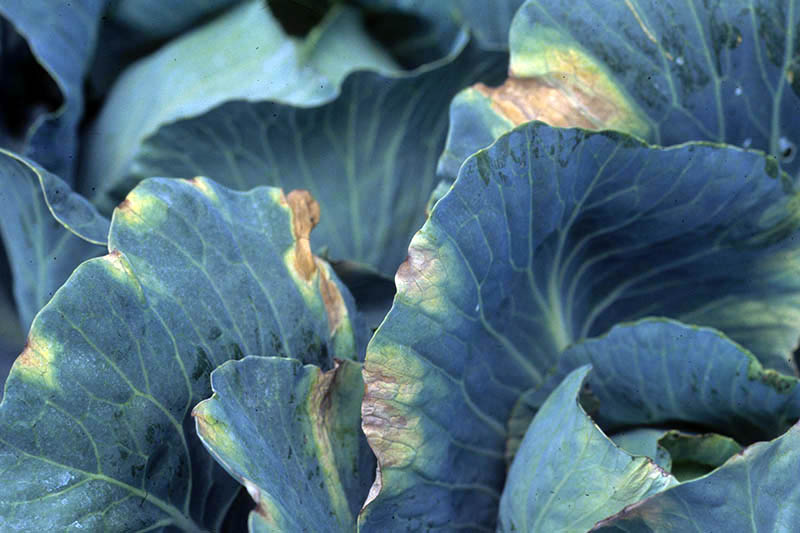

Unfortunately, this affliction can become worse during storage, resulting in heads that are inedible.
The beginning symptoms involve yellowing of the foliage margins, which then spread to the center of the foliage. A classic symptom is a yellow "V" at the midrib of the leaf.
Next, the vascular system turns black, and the infection so spreads throughout the whole constitute.
These bacteria are easily spread in the field past insects, animals, irrigation, pelting, and gardening equipment. Blackness rot can infect plants naturally through stomata at the leaf margins, or through mechanical injuries.
Given the potential severity of this blazon of infection, seeds are unremarkably tested for black rot.
Planting high-quality seed that does non comprise X. campestris pv. campestris is disquisitional, and crop rotation will assist to protect against infection.
You also have the selection of planting varieties of cabbage that are resistant. These include 'Bobcat,' 'Guardian,' and 'Defender.'
'Titanic ninety,' 'Superkraut,' 'Superdane,' 'Roundup,' and 'King Cole' have likewise been shown to be highly tolerant of this affliction.
You tin can learn more about how to manage black rot in cabbage in this guide.
half dozen. Bottom Rot
A widespread soil-borne fungus, Rhizoctonia solani, is specially destructive to cabbages. Plants can contract an infection from contaminated soil.
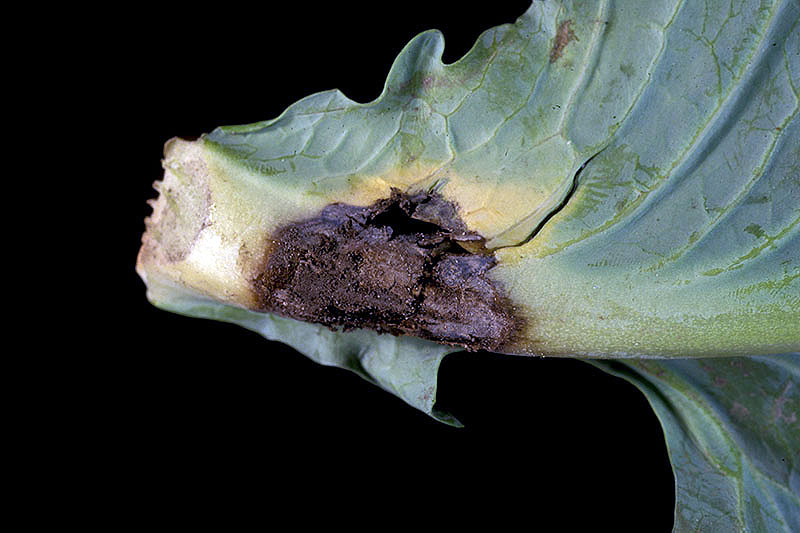

The initial symptoms are tan or brown lesions on the outer leaves. Then the mucus invades the center of the head, which can rot completely within x days.
Plants are more than probable to become infected when the leaves and the soil are moisture, and temperatures range from 68 to 82°F.
At that place are no controls bachelor in one case an infection has started.
Planting in raised beds will help to protect your crop, considering the soil will typically drain better than it would if you were to plant direct in the basis. Wherever you lot plant, well-draining soil is crucial.
Keeping your ingather healthy and providing the proper amount of fertilizer will also aid to keep this illness at bay.
Meet our guide to growing cabbage for more planting tips.
seven. Clubroot
Cabbages are especially vulnerable to clubroot, a illness caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae, a water mold that tin can live in the soil for over 18 years subsequently infecting a crop.
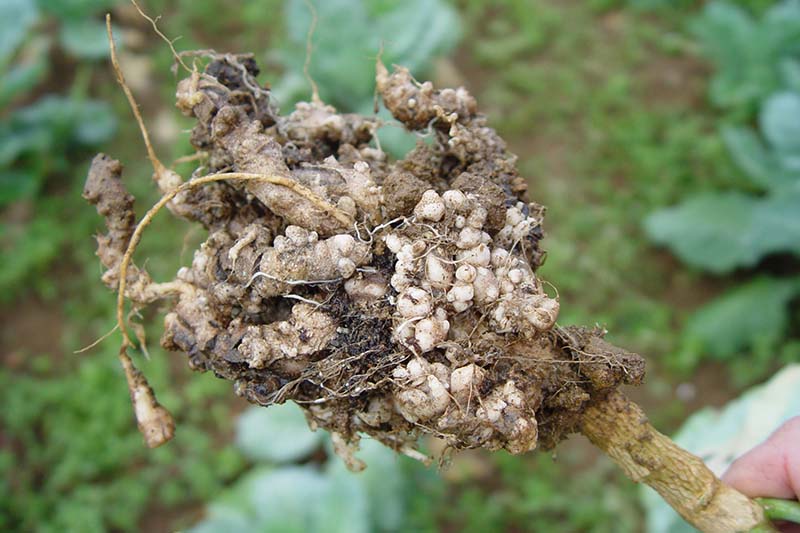

This pernicious and long-lived illness can be difficult to detect. Older plants that are infected will wilt on hot days, only they can frequently announced to recover afterwards the sun goes downward.
The pathogen enters the root hairs and so forms large social club-like galls that tin exist as big as v or six inches wide.
The roots don't office properly, and are also left vulnerable to infection by other soil-borne pathogens.
Infected seedlings take virtually three weeks to show signs of root swellings, and they will typically die. If they survive, yields tin be greatly reduced because growth is stunted.
Infections occur when the plants are exposed to spores released from infected roots. Irrigation water, tools, or even footwear tin spread these spores.
Crucifers are more probable to become infected when they are growing in acidic soils with a pH of vi.five or less.
Once a crop becomes infected, there are no effective control methods available. Since the about common source of infection is infected transplants, you should accept care to utilise clean trays and seed starting media.
Do a soil examination to cheque the pH of your soil, and meliorate the soil with lime as needed, to raise the pH to at to the lowest degree 7.0 before planting.
Lime inhibits the development of this affliction, just information technology volition not prevent clubroot entirely if there are already a large number of spores present in the soil.
Practise a long crop rotation if yous have found an infection in your vegetable beds – wait to plant cabbage in the aforementioned location once again for vi years or more.
eight. Featherlike Mildew
Peronospora parasitica is a h2o mold (oomycete), an organism previously classified every bit a fungus.
This serious illness starts out as lesions on the upper surfaces of the leaves, while the bottom surfaces have white to gray masses of fungal spores visible on them.
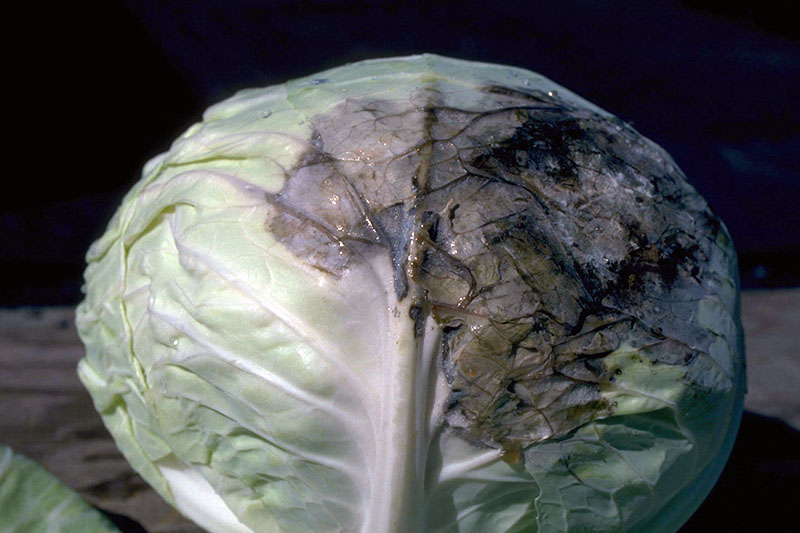
If your seedlings are infected, the whole vascular system can plow black. You may not be able to eat your cabbages if they contract featherlike mildew.
Fog, heavy dew, high humidity, and drizzling rains all favor the development and spread of downy mildew. Ideal temperatures for infection range from 46 to 61°F at nighttime, paired with daytime temperatures of 75°F or less.
Featherlike mildew is a particular problem in autumn crops in areas with wet and mild winters, like Washington State. The pathogen tin continue infecting crops throughout the wintertime, and this can fix the stage for severe infections in the spring if the weather condition are right.
To make matters worse, white rust tin colonize host plants that have been weakened by downy mildew.
There are steps yous can take to preclude downy mildew, such as eliminating cruciferous weeds, and giving plants plenty of space to grow rather than packing them too tightly together. Proper airflow will reduce humidity and make infections less likely to occur.
Another option is to plant your crop in the spring and harvest in the summertime.
If your cabbages are infected with featherlike mildew, y'all can use fungicides to control it.
Read more than most downy mildew here.
9. Mosaic Virus
While a number of different viruses can infect cabbage, you are well-nigh probable to meet mosaic virus.
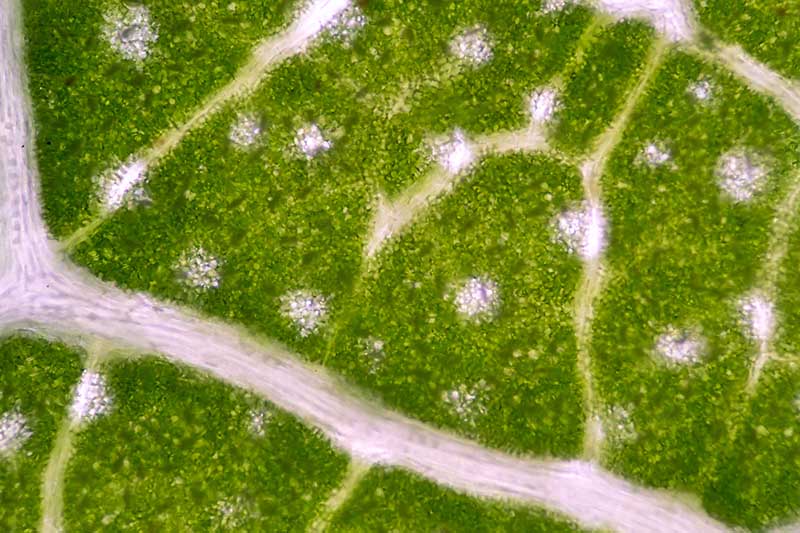

Unfortunately, there is no cure for the virulent pathogens that cause it, so taking steps to prevent the occurrence of this disease is your best bet.
Mosaic viruses spread from weeds like wild mustard, wild radish, or shepherd'south handbag. Controlling all cruciferous weeds will assistance to reduce the likelihood of your cabbage plants becoming infected.
The about common viruses of this blazon to set on cabbage plants are cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) and turnip mosaic virus (TuMV).
Infections tin be difficult to observe early on in the flavor. Nevertheless, later on, the veins will appear clear. The first sign of this is often located at the base of a leafage.
Next, nighttime green areas will become visible along the veins, and dead spots will develop on the leaves. In addition, growth can become stunted.
The outer leaves can develop lesions of dead tissue that are institute throughout the whole head. Stored heads may take dead spots on the internal leaves.
Many types of aphids can spread CaMV and TuMV betwixt weeds and crops. Particular threats include cabbage aphids, green peach aphids, and false cabbage aphids.
These aphids can transmit the virus within a minute of feeding on an infected constitute.
Symptoms are the nearly severe in temperatures ranging from 68 to 82°F.
Mixed infections with cauliflower mosaic and the turnip variety often occur, which results in even more astringent symptoms than either virus alone would typically crusade.
There is no cure for mosaic virus, only decision-making aphids with insecticides tin can help forbid infection. Purge whatsoever cruciferous weeds from your garden, and dispose of leftover crop debris as soon every bit y'all harvest.
Learn more almost turnip mosaic virus in our guide.
10. Phytophthora Root Rot
The water mold, or oomycete, Phytophthora megasperma, causes root rot on cabbages and many other cruciferous plants. It survives the winter equally resting spores within root tissue.
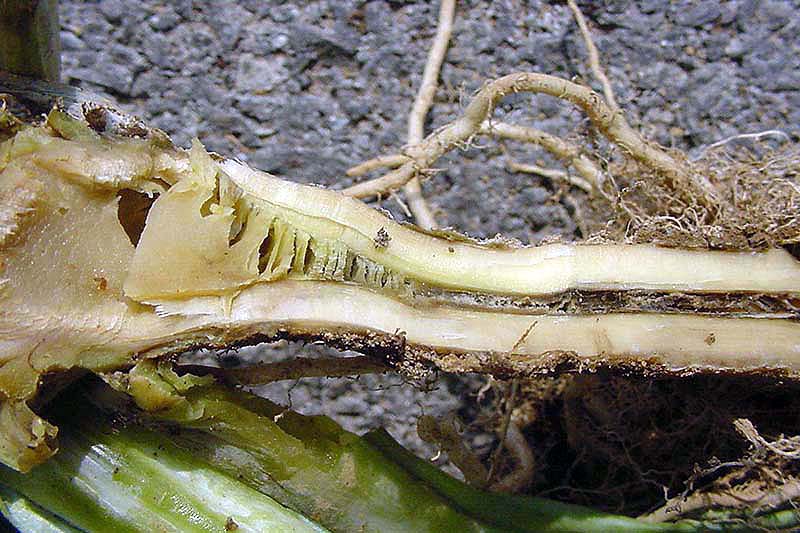

When conditions are correct, such equally when the soil is wet and temperatures range from 55 to 77°F, another kind of spore is released – the pond type known as zoospores.
The zoospores swim through the h2o to infect the roots. The starting time symptoms you lot might run across are discoloration of the margins of the leaves, irresolute to red and purple as the roots die.
As symptoms progress to the stem, the leaves die back. Plants that are infected mostly wilt and often dice.
Anything that promotes good soil drainage will aid protect against this type of root rot. For example, you can cultivate the soil at planting fourth dimension then it won't be compacted, or consider planting in raised beds. And it is too of import to avert excessive irrigation.
If you know that a field or growing area is infected with Phytophthora, don't abound crucifers there, and rotate to non-susceptible crops for iii years.
Y'all can also utilise soil treatments like copper sulfate, according to parcel instructions, to help manage this affliction. Treatment may non save an infected plant, only information technology may preclude it from spreading to neighboring plants.

Southern Ag Liquid Copper Fungicide
Copper sulfate made past Southern Ag is available on Amazon.
Another choice is Monterey Agri-Fos, also bachelor on Amazon.
eleven. Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is caused by Eryisphe cruciferarum, a type of fungus that requires a live host, so it will not typically impale your cabbages.
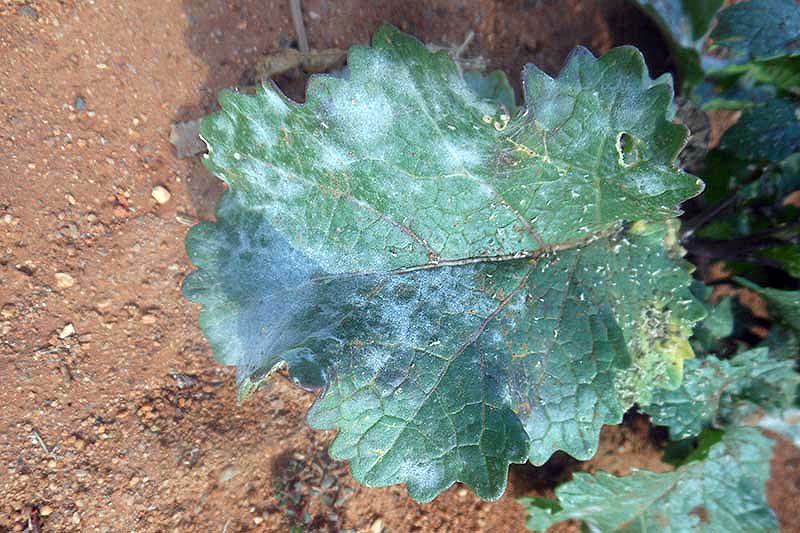

However, you are well advised to grow resistant varieties, since infected plants will produce smaller heads.
Symptoms starting time every bit white lesions on the top of the leaves. As the fungus develops and spreads, the leaves will appear powdery white on both sides every bit they are covered in spores.
Crops are more likely to get infected when they are stressed for h2o. The fungus typically overwinters in cruciferous weeds, and the spores are blown to their hosts.
Powdery mildew typically develops at 59-68°F when there is petty rainfall and low humidity.
Fungicides are not typically required, just if the infection is severe, you can utilise neem oil to the infected plants.
Purging host plants like wild radish or wild mustard will cutting down on the likelihood that your crop will become infected.
Avoid drought stress by irrigating regularly, and don't use also much nitrogen fertilizer.
12. Band Spot
Band spot is acquired by the fungus Mycosphaerella brassicicola.
Cabbages become infected in the garden, but this status can develop into a rot when the heads are placed in storage, leaving them leathery and shriveled with dark lesions.
The first symptoms of ring spot are rings on the stems and leaves that appear water soaked, surrounded by yellow halos.
With farther spread, the lesions may abound and merge together, causing the entire plant to plow black.
Cabbages are more likely to become infected with band spot when the atmospheric condition is moist and cool, with temperatures ranging from 59 to 70°F.
Removing infected plants and destroying all crop debris volition help prevent the spread of this pathogen.
13. White Mold
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a very common fungus that tin can infect more than 300 different institute species. While white mold infects cabbages in the field, it can also crusade losses in storage.
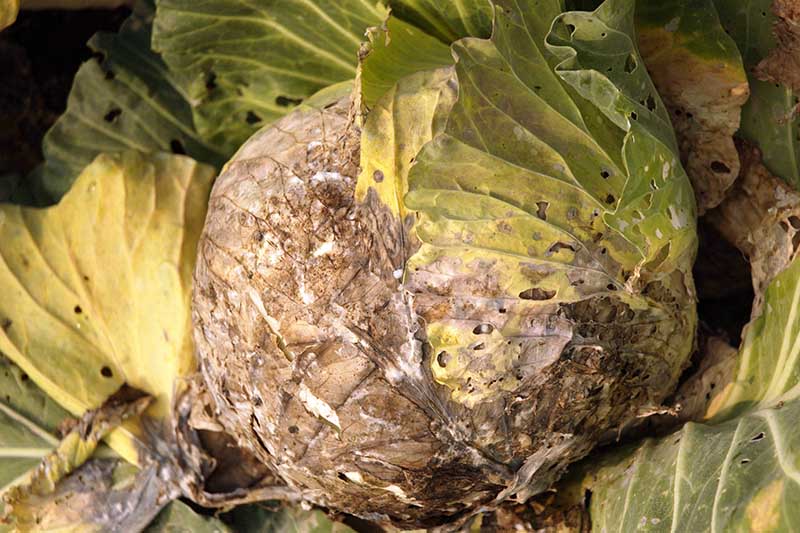

Sclerotinia is a problem in moist weather condition at temperatures of l to 77°F.
The fungus first infects the stem. From there, information technology can spread both downwards to the roots and upward to the leaves, causing them to wilt and resulting in the plummet of the plants.
Symptoms include white cottony growth, which tin be found on or within of the tissues. This is what gives the disease its name.
Part of what makes this disease so pernicious is that the fungus produces reproductive structures chosen sclerotia. These look like black seeds and can live in the soil for years. Sometimes these sclerotia are visible in the infected tissue.
Moisture weather condition favor infection. If the weather turns dry after an infection sets in, you might see brownish cankers on the stalk that do non progress further.
Control for Sclerotinia involves a combination of cultural methods – good sanitation, well-draining soil, weed management, and long crop rotations. Cultivating the soil earlier planting will help to provide good drainage, which is essential to prevent a buildup of moisture.
Early handling at the onset of an infection is likely to be more successful than attempts to care for a severe infection that has already progressed significantly.
Y'all tin employ a combination of fungicides and biopesticides to control white mold. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis treatments may prove effective.
Benomyl is a fungicide that has been recommended to treat while mold on cabbage, but you may want to double check with your local extension office to determine which fungicides are registered to treat this disease in your surface area.
14. Yellows
Yellows is caused past Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans, a fungus that lives in the soil. Its spores can survive for many years.
At that place is no practiced control method for yellows on cabbage, and planting resistant varieties is your best bet to avoid this disfiguring infection.
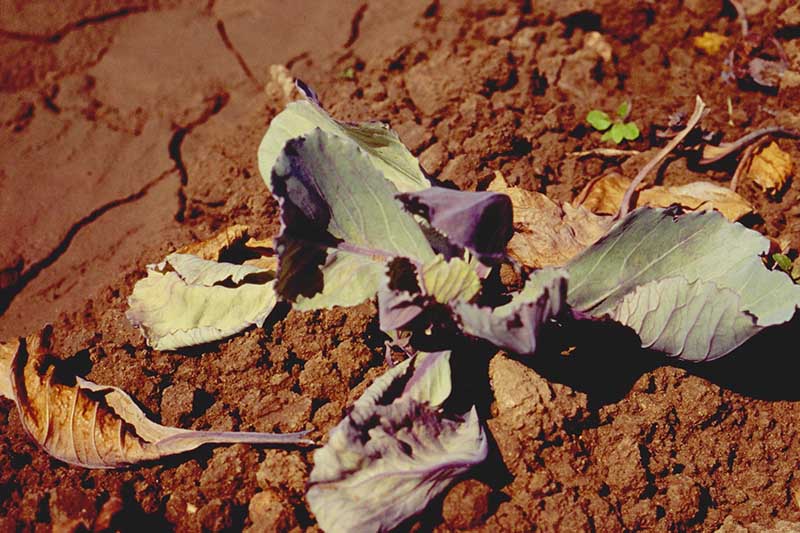

This pathogen invades the vascular system and tin can often kill its host outright.
Plants that survive will have leaves that are dull and yellowish. Starting at the base, these leaves may die early. The survivors are frequently yellowish on 1 side of the found, with stunted growth.
This is a disease that favors warm temperatures, and it is less likely to occur when temperatures are beneath 68°F.
Healthy Garden, Good for you Heads
Like other cole crops, cabbages are vulnerable to a number of diseases caused by a variety of different pathogens.
Practiced gardening practices such every bit keeping weeds and pests at bay, sanitizing your equipment, and preventing wet buildup can help to forbid outbreaks.
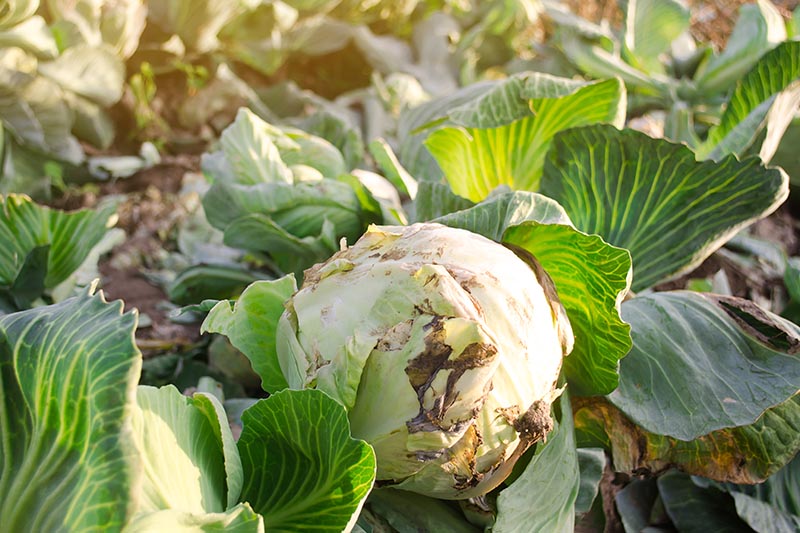

Rotating your planting area with other types of crops is essential if you lot want to abound cabbage in a location that has been previously infected.
Have your cabbages suffered from whatever of these diseases? Let u.s. know how they fared in the comments below.
And for more information almost growing cabbage in your garden, check out these guides side by side:
- How to Place and Control Mutual Cabbage Pests
- Reasons Why Your Cabbage Plants May Not Form Heads
- How to Grow Winter Cabbage for a Belatedly-Season Harvest
- How to Keep Slugs off Cabbage and Other Cole Crops
© Enquire the Experts, LLC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Meet our TOS for more than details. Product photos via Bonide and Southern Ag. Uncredited photos: Shutterstock. With additional writing and editing by Allison Sidhu and Clare Groom.
Source: https://gardenerspath.com/how-to/disease-and-pests/common-cabbage-diseases/
Posted by: angellounto.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are All The Animals Who Can Get Blackleg"
Post a Comment